Foundation Depth and Integrity Methods
Olson performs a wide variety of Nondestructive Testing (NDT) methods that are applicable to foundation evaluation
We conduct forensic evaluations of existing foundations as well as quality assurance of new construction. We have investigated nearly all types of foundations in use including drilled shafts, auger cast piles, steel and concrete driven piles, mat foundations, spread footers, massive caissons, stone and masonry foundations, etc.

Crosshole Sonic Logging (CSL)
Crosshole Sonic Logging (CSL) is the most accurate and reliable technique for assessing the integrity of deep foundation elements constructed on-site from concrete or grout.
Test for:
- Cracks
- Voids
- Soil Intrusions
- Sand Lenses
- Uncured
- Weak Concrete
- Necking
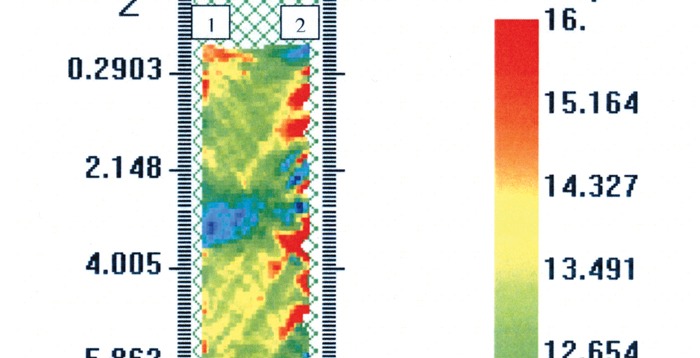
Crosshole Tomography (CT)
Crosshole Tomography (CT) testing and analysis is normally used in conjunction with Crosshole Sonic Logging (CSL) testing to provide additional information as to the size, shape, and location of a defect which has been located with standard CSL testing.
Test for:
- Velocity Tomogram Images of Voids/Soil Intrusions
- Honeycomb
- Cracks
- Uncured or Weak Concrete

Sonic Echo/Impulse Response (SE/IR)
The Sonic Echo (SE) method is normally conducted in conjunction with the Impulse Response (IR) method together as the SE/IR method. These methods are used for low strain integrity testing of piles and deep foundations for length and integrity determination.
Test for:
- Cracks
- Voids
- Soil Intrusions
- Uncured or Weak Concrete
- Foundation Lengths

Ultraseismic (US)
Ultraseismic (US) investigations are performed to evaluate the integrity and determine the length of shallow and deep foundations. This method is a variation of the more typical SE/IR test method, with the US method having a higher sensitivity to weak bottom echoes.
Test for:
- Cracks
- Voids
- Soil Intrusions
- Foundation Lengths

Parallel Seismic (PS)
The Parallel Seismic (PS) method is used for length determination of unknown foundation depths for bridges and buildings.
Test for:
- Length Determination
- Foundation Type
- Scour Evaluation

Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR)
The Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) method as applied to foundation testing is primarily used to map rebar in foundation tops and to measure the depths of abutments, mats, spread footings, and other relatively shallow concrete foundations.
Test for:
- Location and Depth Measurements of Rebar in Concrete
- Thickness and Depth Measurement of Foundations
- Location of Buried Foundations

