Parallel Seismic
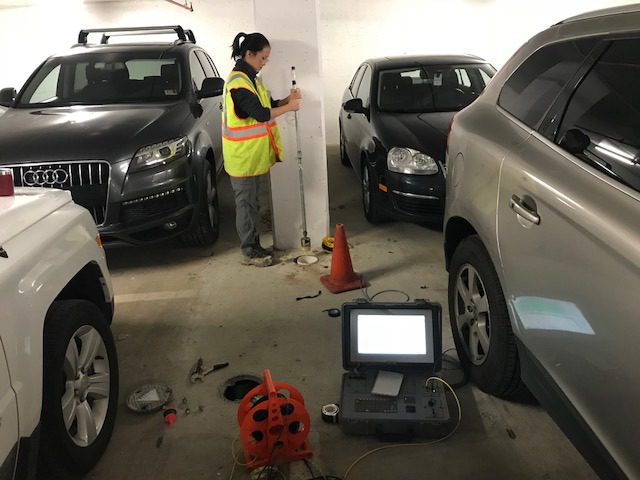

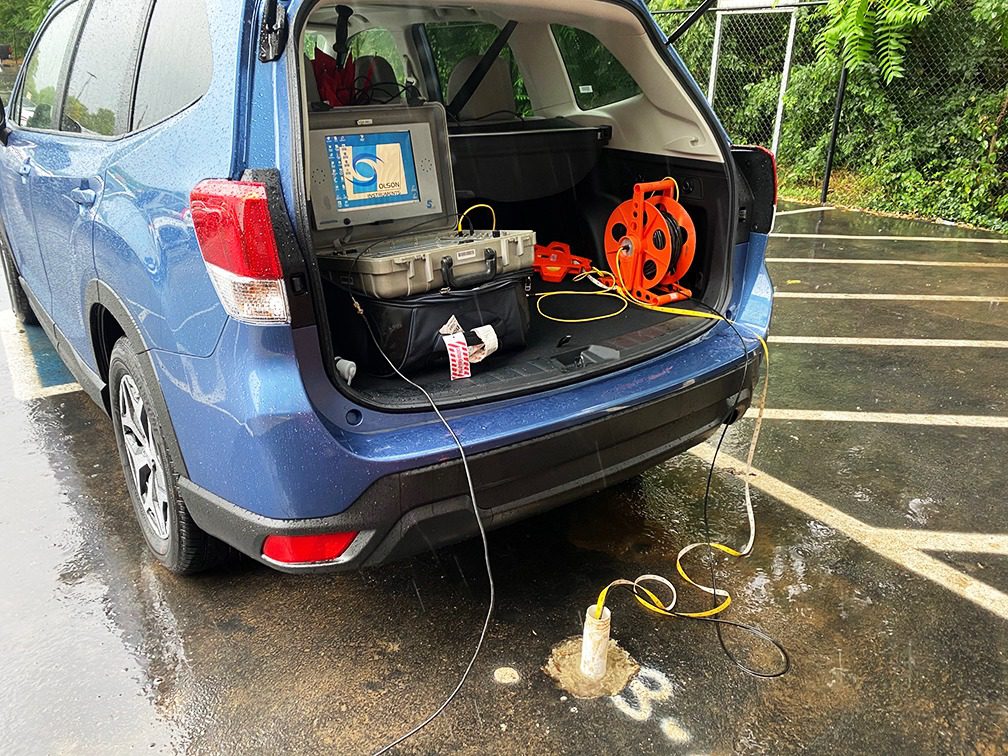
The Parallel Seismic (PS) method is used for length determination of unknown foundation depths for bridges and buildings. The strengths of this method are that it can be used even in cases where the foundation itself is not accessible, and can be used to determine the tip depths of foundations with complex geometries such as piles under spread footings.
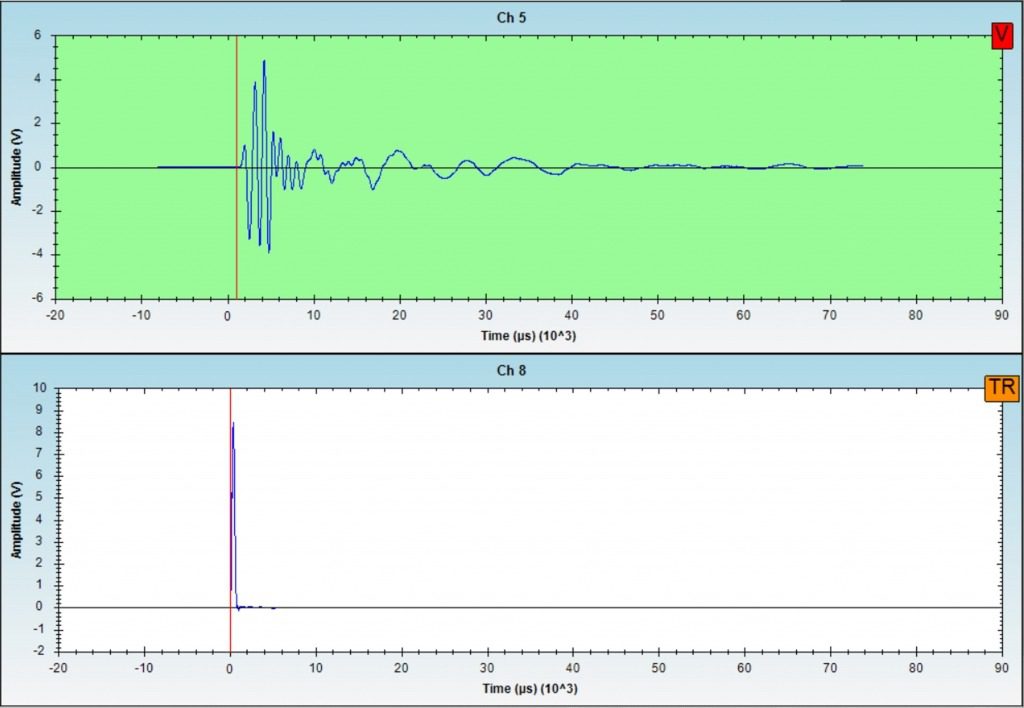
The PS test involves impacting the foundation or the structure connected to the foundation to “listen” for subsequent signal arrivals with a receiver in an adjacent cased borehole. The cased borehole is typically located within 5-7 feet of the edge of the foundation and is drilled to a bottom depth well below the suspected/required foundation depth. The borehole can often be the same borehole used for a geotechnical boring at the site.
A variation of the PS method is the Parallel Seismic / Cone Penetrometer Test (PS/CPT) method, which uses an instrumented cone pushed into the soil as the receiver. With this system, no borehole is required.
Applicable on:
- Deep Foundations of all types
- Abutment Piers
- Sheet Piles
- Footings
Test for:
- Length Determination
- Foundation Type
- Scour Evaluation
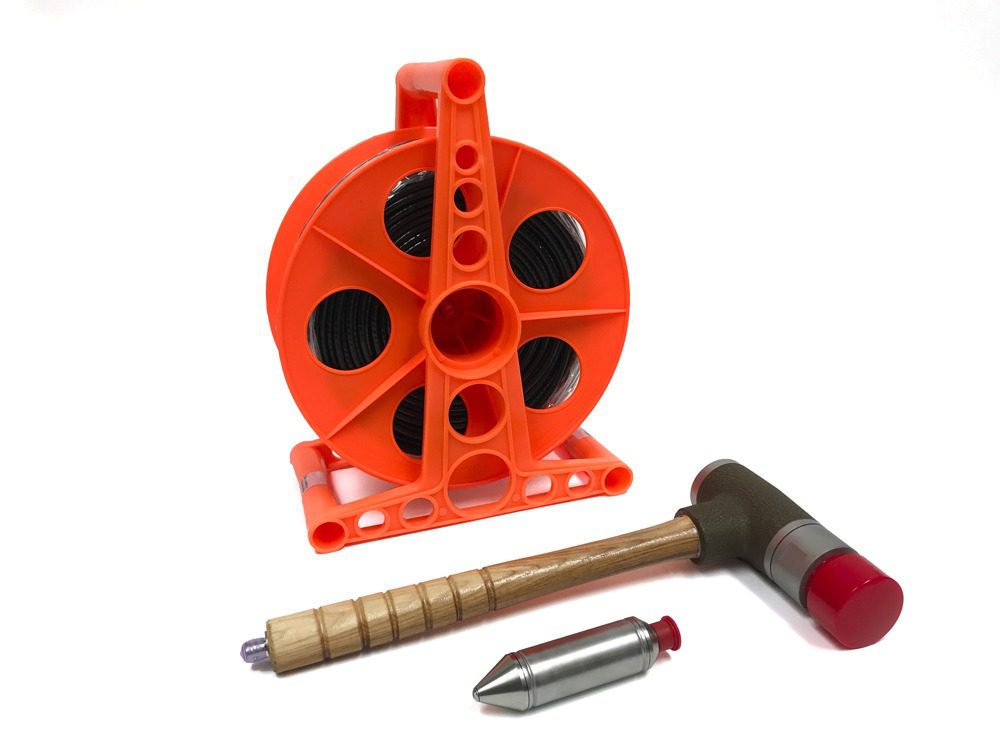

The Parallel Seismic System
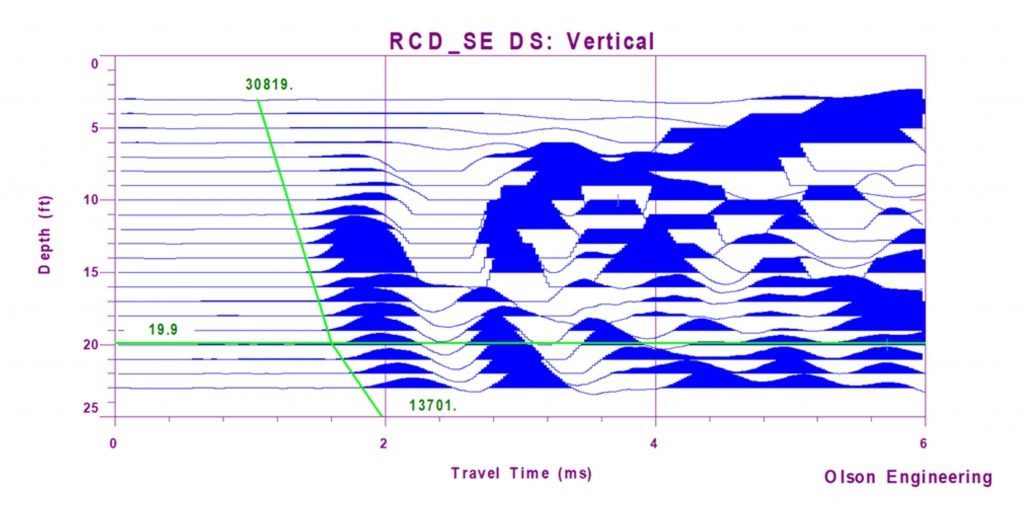
Parallel Seismic (PS) systems are designed to determine the length and integrity of foundations when the top is not accessible or when the pile is too long and slender to test with echo techniques, or below a buried pile cap.
- Convenience
- Determine the length and integrity of foundations when the top is not accessible
- Informative Testing
- This test provides information concerning the length and compressional velocity of foundations
- Variety of Materials
- This system can be used on concrete, wood, masonry, and steel foundations
- Accurate Testing
- The system design allows for fast and accurate field measurements – depth accuracy can be determined within 5% or better
- Additional Information
- This test procedure can provide information about the soil below the foundation bottom as well as the foundation