Structural, Pavement, and Tunnel Methods
Olson offers a large number of Nondestructive Testing (NDT) methods which can be used for structural evaluations.
We have a comprehensive suite of methods to evaluate the condition of walls, slabs, pavements, columns, mats, and other members in all types of structures. These methods can be used on a variety of materials, including reinforced and unreinforced concrete, steel, masonry, etc.

Impact Echo (IE)
The Impact Echo (IE) method is used for rapid flaw detection and thickness evaluation of concrete and masonry structural materials. A variation of the impact echo principle is the Impact Echo Scanning (IES) method.
Test for:
- Thickness and Internal Cracks
- Voids
- Honeycomb
- Delaminations

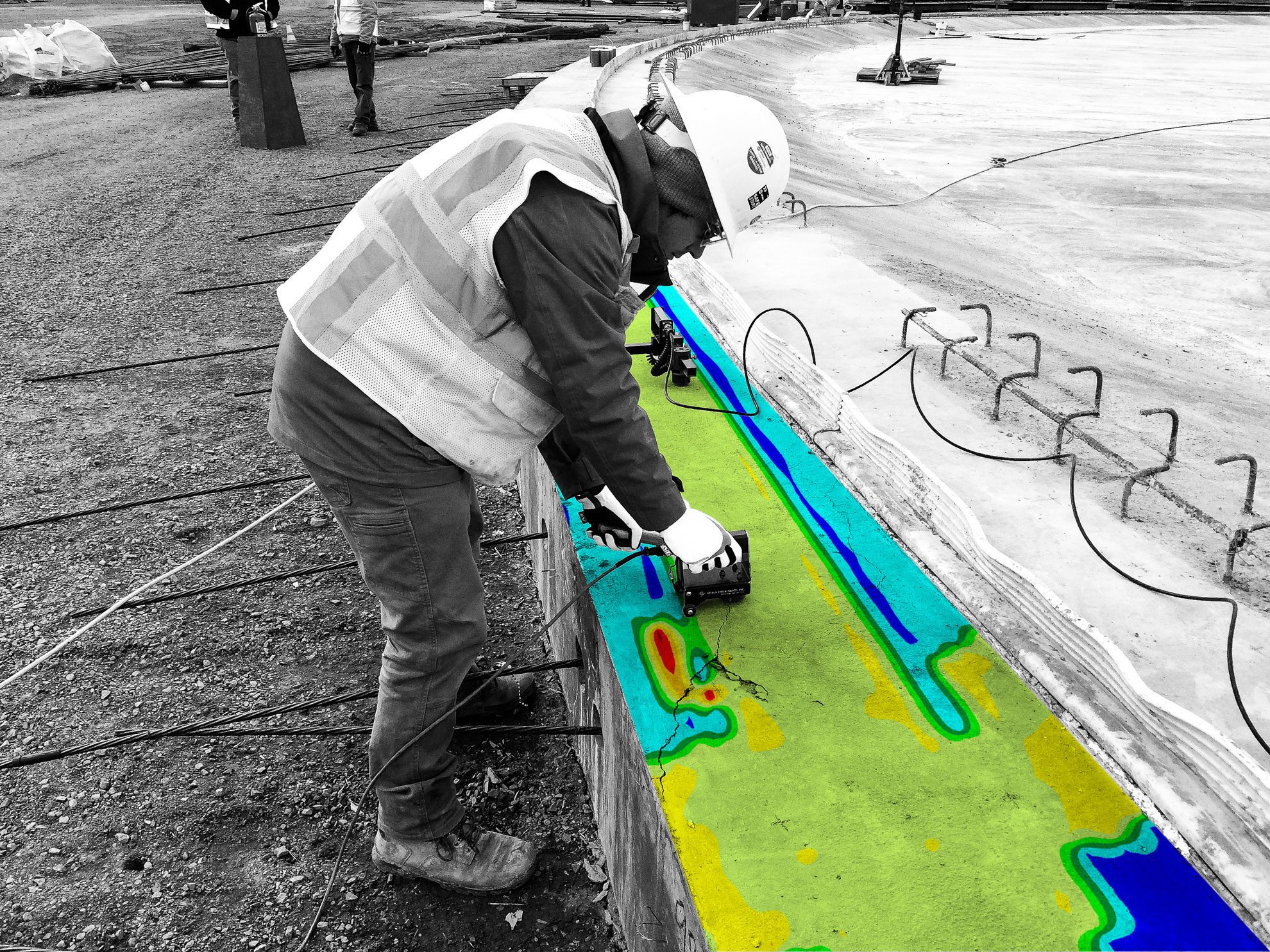
Bridge Deck Scanning
The Olson Sonic Surface Scanner (S3) is the most technically advanced system for structural condition assessment to date. No other system on the market tests for both top and bottom concrete deck delaminations, while performing over 20,000 Impact Echo (IE) tests in 1 hour.
Test for:
- Top Concrete Delaminations
- Bottom Concrete Delaminations

Spectral Analysis of Surface Waves (SASW)
The Spectral Analysis of Surface Waves (SASW) method is used on structural elements to estimate crack and damage depths and to measure relative concrete quality.
Determine:
- Pavement system profiles including the surface layer, base and subgrade materials
- Surface opening crack depths
- Freeze-thaw damage depth measurement
- Fire damage depth measurement
- Abutment depths of bridges
- Condition assessments of concrete liners in tunnels, and other structural concrete conditions

Slab Impulse Response (SIR)
The Slab Impulse Response (SIR) method is used primarily to identify and map subgrade voids below slabs-on-grade.
Utilize SIR for:
- Evaluating the support conditions before and after repairs of slab subgrade
- Looking for low-stiffness areas associated with hidden damage (honeycomb, void, or cracking) for general assessment of concrete structures
- Subgrade void detection and mapping, in conjunction with Ground Penetrating Radar
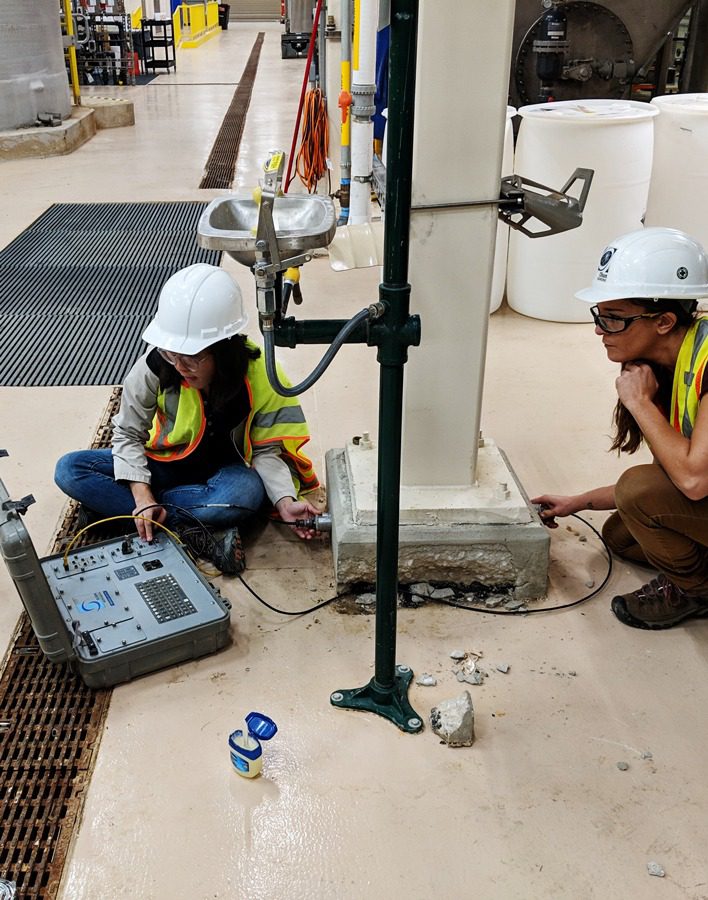

Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity (UPV)
Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity (UPV) testing is used to determine the integrity and quality of structural concrete or stone (up to 6 feet thick) by measuring the speed and attenuation of an ultrasonic wave passing through the element being tested.
Test for:
- Voids
- Honeycomb
- Cracks
- Delaminations
- Strength of Early Age Concrete
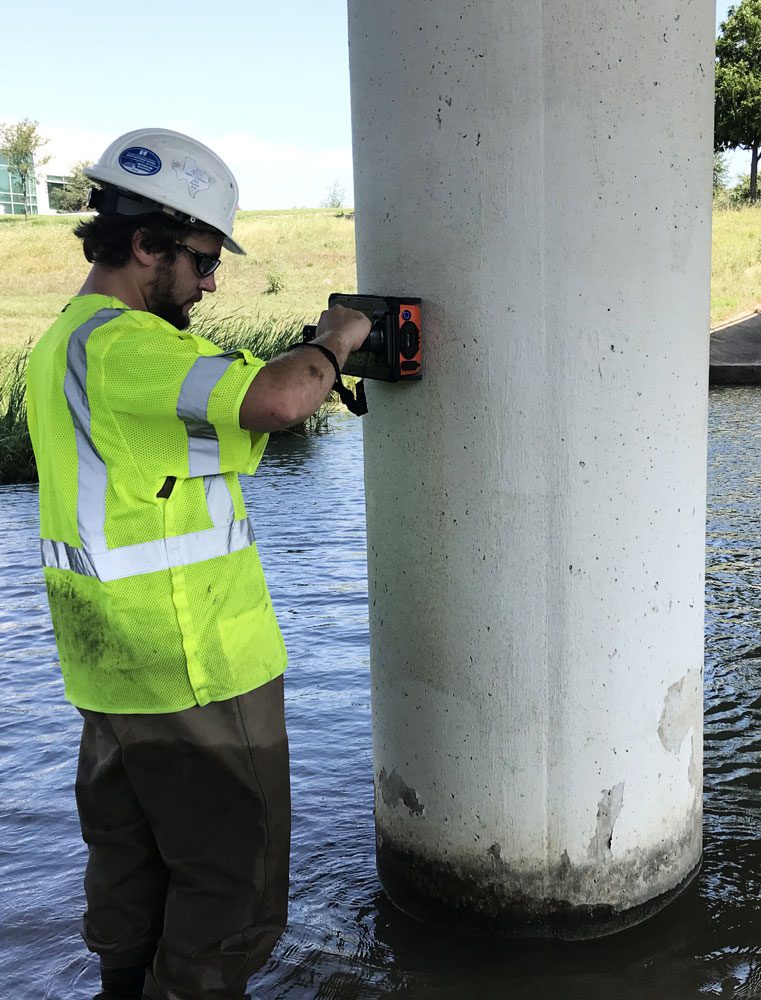

Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR)
The Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) method is primarily used on structures to locate and measure the depth of embedded objects in concrete such as conduits, rebar, and post-tensioning (PT) cables.
Test for:
- Location and Depth of Embedded Features: Rebar; PT Cable; Conduits; Etc.
- Slab Thickness Profiling
- Flaw Location
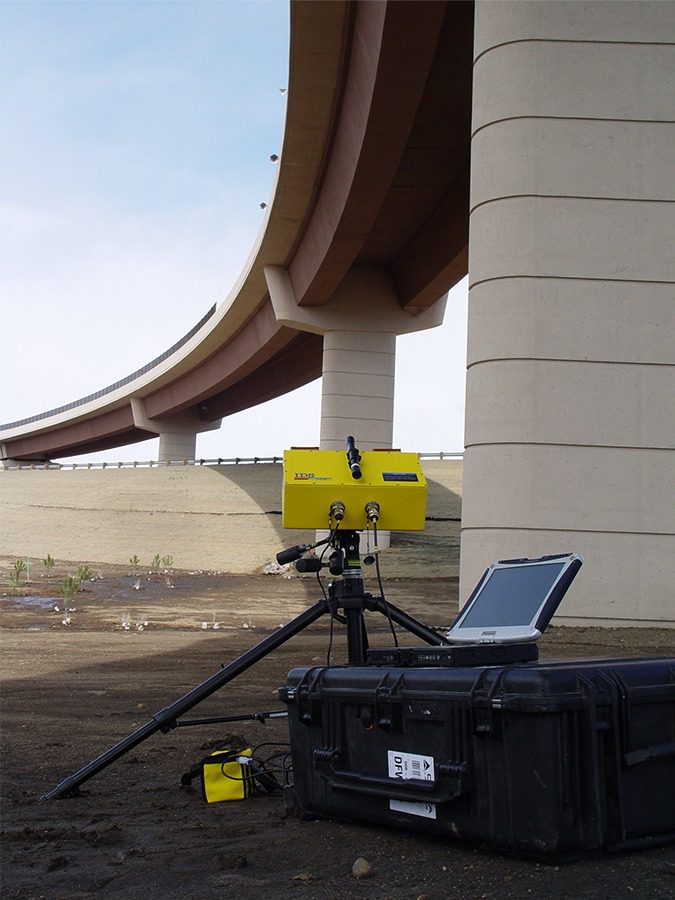

Interferometric Surveys
Olson Engineering has the equipment and expertise to offer remote monitoring by interferometric radar to measure movements in bridges, structures, ports and concrete/masonry dams. Static monitoring services include structural load testing, structural displacement and collapse hazards, and preservation of historic buildings.
Test for:
- Displacement
- Deformation
- Vibration
- Response to Static and Dynamic Load
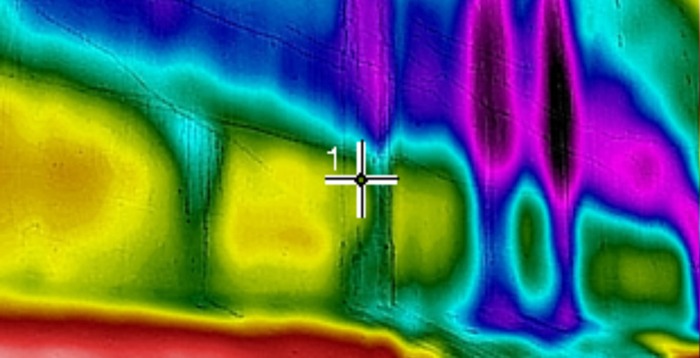
Infrared Thermography (IT)
Infrared Thermography (IT) is a technique used for locating shallow delaminations, cracks, and voids in concrete and other pavements as well as air gaps and voids within concrete slabs, block walls, and other structures. Infrared Thermography senses the emission of thermal radiation from a member and can be used to produce a 2D image from the thermal signal.
Test for:
- Voids
- Delaminations
- Cracks
- Ungrouted Block Cells
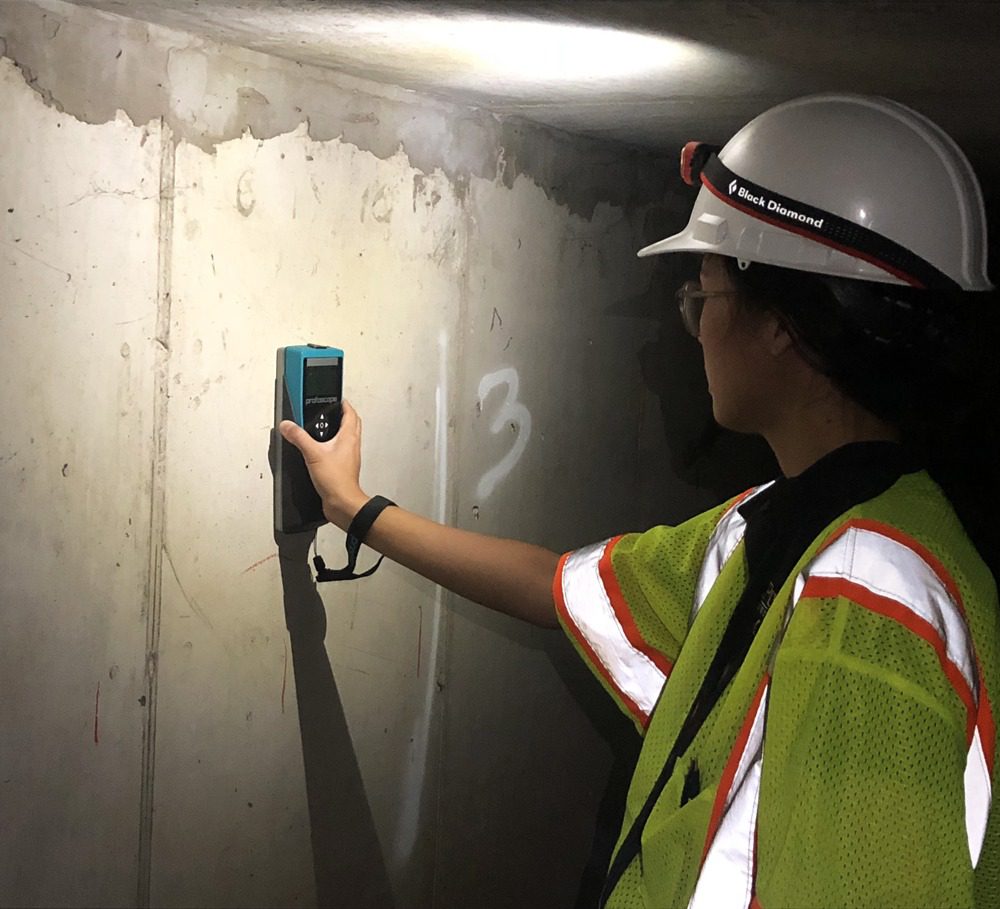

Covermeter (CM)
The Rebound Hammer (RH) method (also known as the Schmitt Hammer method) is used to quickly determine the uniformity of a concrete member with respect to surface strength and stiffness. In addition, from the data collected an estimate of concrete strength may be inferred using standard calibration curves.
Test for:
- Rebar
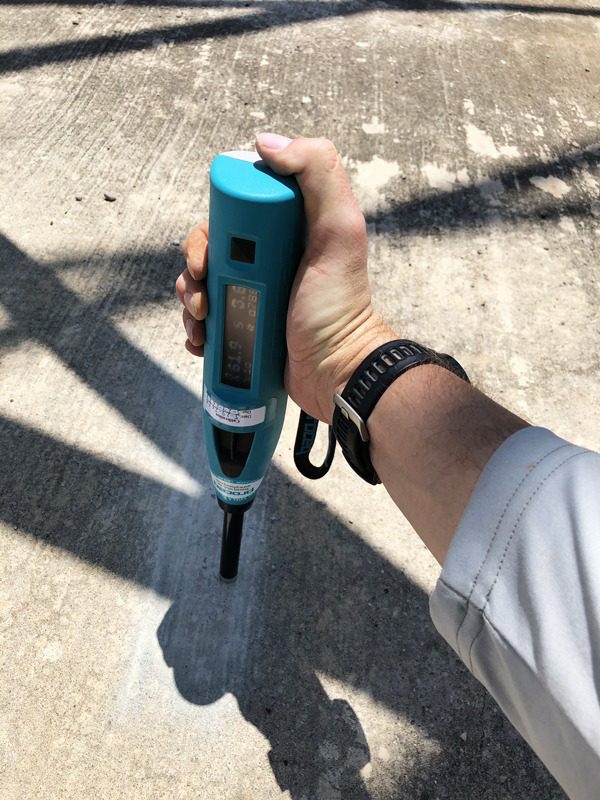

Rebound Hammer
The Rebound Hammer (RH) method (also known as the Schmitt Hammer method) is used to quickly determine the uniformity of a concrete member with respect to surface strength and stiffness. In addition, from the data collected an estimate of concrete strength may be inferred using standard calibration curves.
Test for:
- Concrete Uniformity in Compressive Strength and Stiffness at the Surface
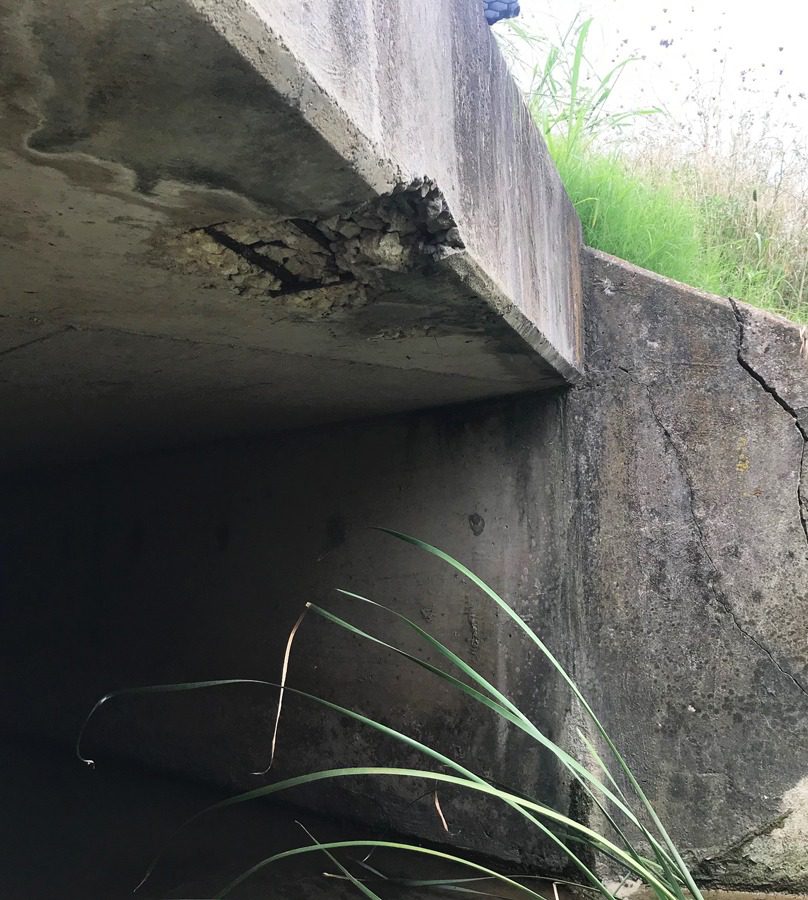

Corrosion
The Half Cell Potential (HCP) method is used when monitoring the corrosion activity, resistivity, and rate of reinforcing and other structural steel elements embedded in concrete. This is an electrochemical technique used to locate areas of active corrosion of steel reinforcement in a concrete slab or wall. A refinement of the basic HCP method is the Galvanostatic Pulse Measurement (GPM) method.
Test for:
- Corrosion Location and Rate of Steel Reinforcement

